
Sacred Texts Evil Index Previous Next
Buy this Book at Amazon.com


The Evil Eye, by Frederick Thomas Elworthy, [1895], at sacred-texts.com
IF so many strange beliefs still exist in these days of science and enlightenment, it is easy to see how in olden times a fanciful people, full of imagination, who personified not only every aspect of nature, but every virtue and every vice, got to look upon the trees or animals they thought sacred, as symbols of the deity to whom they were sacred. Perhaps of all nations we English are the most materialistic and matter of fact, yet in what endless ways do we even now make use of symbols, to denote not only objects, but events and abstract ideas! Every letter that we write or print is said to be the survival of some primitive picture, and thus to be the symbol of a separate idea. In Christian art symbolism occupies as large a place, as in the pagan mythology of old. A figure holding a key with sometimes a cock in the background is at once known as St. Peter; a man in a boat typifies Noah; a figure with a loaf and a basket signifies the feeding of the multitude; the fish is a symbol of our Lord, said to be a Greek acrostic as well as a sign; the dove represents the Holy Spirit; the cross is a symbol not only of a great event, but of a great doctrinal fact; while the hand, or Dextera Dei, of which we have much to
say, represents power, and thereby the person of the Almighty Father.
Even latter-day Puritans, "who are eager to banish the cross and the crucifix, with everything that has to them even a faint association with the terrible word idolatry, 182 accept that most symbolic of romances, The Pilgrim's Progress, as a true exemplar of their special views," and thus provide the best possible evidence that no religious feeling worthy of the name will consent to live without some imaginative expression for those urgent and intimately varied spiritual yearnings, for which there is no definite and rigidly accurate language.
This love of symbol and the eagerness for its artistic use are said to be rapidly reviving 183--a fact which does but prove how history repeats itself, and that the primitive notions of mankind are constantly reasserting themselves; that we are but now readopting the methods which have prevailed intermittently throughout all human time.
In this way we get a clue to the primitive use of emblems and symbols by way of protection, against evils that people believed might be averted, through the intervention of the powers or divinities to whom they specially appealed; hence the reverence for, the half-worship of, the symbols representing those powers to their own minds. Moreover the uncultured mind does not readily discriminate between the symbol itself and the person, object, or fact which it is intended to represent.
In view of the looseness with which words of
different significance are often used to represent the same ideas, and, on the other hand, the same word used to imply different meanings, it is well here to define what we mean by emblem and symbol. Curiously both words were originally derived from concrete objects, very far removed from the ideas they ultimately came to signify. Symbol properly means the separate contribution of each person towards the cost of a Greek drinking party. To ensure due payment it was customary for each person to pledge his signet ring to the caterer, to be redeemed on his paying his share of the bill. This custom was also adopted by the Romans, and by the time of Plautus the ring itself had got to be called symbolum. The signet ring having thus become the most easily available, as well as trustworthy of credentials, symbolum developed quickly into signifying the credential itself. From this, by a further development, in ecclesiastical language, as in the Symbolum Apostolicum, it expressed a definite creed, and at last has become a term for the conveyance of any idea, but more particularly of such as appertains to religious belief. We may now define a symbol as a means of conveying ideas and facts to the mind, through representations more or less pictorial. By constant repetition these pictures become in a way so conventionalised and stereotyped, that the mere portrayal, or even the mere mention, of a certain object conveys a distinct and well-defined train of thought to the mind.
An emblem was an inlaid or raised ornament on a vessel, but inasmuch as the subjects of the designs were always figures of persons, generally mythological, so the word emblem came to imply representation,
more or less allegorical, of some person or attribute personified; and in the end, by the same process of repetition, the emblem became conventionalised like the symbol, so that certain representations always conveyed to the beholder the idea of a certain fact or event, or of some being, or personification; with this difference, that the emblem expressed more fully and distinctly, while the symbol only hinted at the idea conveyed. 184 To make what we mean more clear, the crucifix is an emblem, a dramatic representation of a great event, carrying with it all its history and consequences, while the simple cross is a symbol no less expressive, but yet conveying by a mere hint all the history, all the doctrine, all the significance, of the more elaborate representation.
Justice, again, as an emblem is represented as a blindfolded female figure, holding the sword of punishment in one hand, with the balance of judgment in the other. As a symbol of justice, either the sword, or the balance alone, conveys the idea, though in a more abstract form. Victory, too, has for her emblem a winged female figure holding a wreath or a palm branch, while the symbol of victory is the wreath or the palm alone.
It will be readily understood how a symbol may be easily developed from an actual pictorial emblem, into a mere description, either spoken or by gesture acted, so as to convey the same idea. Thus when the hand is raised in the act of benediction, the three
extended fingers are the well-known symbol of the Holy Trinity; so when we speak of bearing the cross, wearing the wreath or the palm, we symbolise and convey our meaning just as clearly as though those symbols were actually painted or carved.
Precisely as a miniature in a locket brings back to the wearer the individuality of the person portrayed, so does the symbolic representation of the deity, whose aid is sought, bring back to the mind of the beholder the whole conception of the attributes and power of the being so represented. An ancient Roman believed that Juno would protect him against certain dangers; forthwith he paints or carves a peacock, her own bird, and is thus reminded of her. In theory he prays to her as often as he looks upon her symbol, while he honours or worships her by wearing it. 185
The practice, if not the belief, still survives amongst us.
Some eight or ten years ago a gentleman well known to me went to call on an intimate friend of his. Unfortunately for him, he had the eye of a peacock's feather in his hat. When the lady of the house saw it, she snatched it from him and threw it out of the hall-door, rating him as if he had been guilty of some great moral offence.
Some years ago, in North Yorkshire, an old servant came to the house where I was, and found some peacocks' feathers above the mantelpiece in one of the bedrooms. She expressed her horror to the young ladies of the house, and said that they need never expect to be married if they kept such things for ornaments. 186
In Shropshire also it is believed to be very unlucky to bring peacocks' feathers into the house. 187
No doubt the belief that to keep peacocks' feathers is unlucky, comes from the ancient cult of Juno--her anger being in some way excited by the plucking of the feathers of her favourite bird; while the idea that so long as they are kept in the house no suitors will come for the daughters, points to the old attribute of spite and jealousy in love or matrimonial matters, with which that goddess was always accredited. 188
From keeping and using such objects or signs, as reminders of the worship due to the beings symbolised, the history of the word symbol shows that it is but a very short step to the belief in the efficacy of the symbol itself, and hence we are led to the universal use of what have been of old called amulets.
These are described 189 as "anything worn about the person as a charm or preventive against evil, mischief, disease, witchcraft," etc. In Smith's Dictionary of Antiquities we find it said that the word signified something suspended, and that it was used for objects such as a stone, plant, artificial production, or piece of writing, which was suspended from the neck, or tied to any part of the body--seemingly ignoring the many other uses of amulets both ancient and modern. Even in Pliny's time amulets were not merely worn, but were used as ornaments or objects having special purposes, fixed or otherwise, as they are to this day, about the houses, carriages, and fields of widely diverse races. The word amulet is nowadays very
commonly used as synonymous with talisman, whereas in meaning it is entirely distinct. The latter means a "sigil engraved in stone or metal," 190 and it served a double purpose, namely, "to procure love, and to avert mischief from its possessor," while an amuletum, derived from amolior to do away with, or to baffle, 190a had for its sole end the protection of the owner. Pliny, writing on the cyclamen (tuberterræ) 191 says, it "ought to be grown in every house, if it be true that wherever it grows noxious spells can have no effect. This plant is also what is called an amulet." Boccaccio speaks of "the skull of an ass set up on a pole in a cornfield as a potent amulet against blight." As a modern parallel to this we are told that at Mourzak, in Central Africa, the people set up the head of an ass in their gardens to avert the evil eye from their crops. 192
 Click to enlarge FIG. 7.--King's Handbook of Gems. |
similar intention. 194 The grillo or locust is said 195 to have been adopted as an amulet from its likeness to a skeleton, which is still the emblem of Chronos or Saturn, and a powerful charm against the evil eye.
The Maltese, who are full of beliefs about the
 Click to enlarge FIG. 8. |
We are told 198 that "the ear-rings" mentioned in Gen. xxxv. 4 and Hosea ii. 13 were really amulets, and were connected with idolatrous worship. Amulets, however, were mostly worn round the neck, or rather suspended from a necklace and forming its centrepiece. We find this custom coming down to us here in England, through the classic and Middle Ages to our own times, though just now out of fashion, in the various lockets containing hair, etc., with other articles of a like kind forming the central ornament of necklaces. In some
countries these things are still worn, not as mere ornaments, but avowedly as protective amulets against dread fascination. By no means were all hung round the neck, for the phylacteries which were worn as the "frontlets between thine eyes" (Exodus xiii. 16) were true amulets. One kind of phylactery was bound upon the bend of the left arm, and the other on the forehead. They were little leather boxes containing strips of parchment on which were written the four following passages of Scripture, called the Tetragrammaton, namely, Exod. xiii. 2-10 and 11-16; Deut. vi. 4-9 and xi. 13-21. They were certainly worn by all Jews over thirteen years of age in the time of our Lord. 199
Slips from the Koran, the Scriptures, or other writings, are now worn on the person, or upon horses and camels, by Arabs, Turks, Abyssinians, 200 Greeks, Italians, and even English. They are all avowedly worn for the purpose of averting the evil eye; and seeing that the dread of it was perhaps even greater in old days than now, it seems but reasonable to assume that the direct object of the biblical phylactery was then, as it is to-day, to baffle the malignant glance.
It is curious that Turks, and, indeed, all Mahomedans, once used animals and figures of men, representing various deities, as amulets against fascination, but since their conversion from heathenism they have discarded most of these, and now wear sentences from the Koran, avowedly to guard them against the evil eye. Little silver cases to contain them, such as are shown on Fig. 112, p. 259,
are regular articles of sale in all Eastern bazaars. At Constantinople they may be bought by the dozen.
It was said by Plutarch 201 that when Isis brought into the world Harpocrates, the posthumous son of Osiris, she wore an amulet round her neck, in the shape of a vase, the "emblem of Ma," the goddess of truth. The vase was also a symbol of Osiris. 201a This vase represented water; hence the vivifying power of nature, i.e. Osiris the personification of the Nile 202 which was thus typified by a vase.
Among the ancient Egyptians not only were protecting amulets worn by the living, but in that land where the belief in a future life seemed to absorb so much of the care and interest of the present, they placed them in profusion on their dead, in order that they might be protected from evil spirits and the blighting eye, during the dark passage from this world to the next.
Maspero 203 says these amulets (speaking of scarabs)
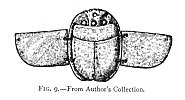
Click to enlarge
FIG. 9--From Author's Collection.
were "symboles de durée présente ou future," placed, ailes déployées, upon the breast of the dead along with a written prayer (Fig. 9), that the heart (of the
person) whose form the beetle was made to represent, would never bear witness against the dead in the day of judgment. The commonest of all Egyptian amulets, except the scarab, was that known to English people as the Eye of Osiris: "L'œil mystique (Fig. 10), l'ouza lie au poignet ou
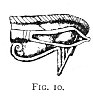 Click to enlarge FIG. 10. |
We find the eye also used for two other signs in Egyptian writing. It was said to be that of Shu or Horus as the god of stability, and was carried in funeral processions along with the sacred boat. 206 Wilkinson says it "was placed over the incision in the side of the body when embalmed, was the emblem of Egypt, and was frequently used as a sort of amulet and deposited in the tombs." 207
It was natural from the association of idea with fact, or "sympathetic magic," that representations of the eye itself should among all people have been considered potent amulets against its malign influence. The Phœnicians certainly used it as an amulet. In the Museum at Carthage, among the objects found in the ancient tombs, there are
 Click to enlarge FIG 11. |
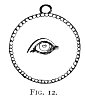 Click to enlarge FIG. 12. |
In the Louvre among the gems is a medal-shaped amulet (Fig. 12), with an eye alone in the centre; and Jahn gives several other examples of the single eye used as an amulet, especially in two necklaces drawn on Taf. V. of his article. In one, the eye is
the pendant to a necklace formed of conchæ veneris; this latter (Fig. 13) a potent charm in itself against
 Click to enlarge FIG. 13. |
As we proceed with the consideration of the various charms and amulets used by ancients and moderns alike, we shall find that not only were single objects, such as the eye, the hand, and many others to which we shall refer later, used as such, but that there was a combination, a sort of piling up of emblems and symbols, so that we constantly find objects of a highly composite character differing very essentially in their several component parts, but yet on the whole presenting a sort of similarity; while it is perfectly obvious that the design or purpose of these compound amulets was in all cases the same.
We shall endeavour to discover as we go on what was the special import of each item of these many compounds, and as far as possible to decide what deity was typified by the several representations made use of--for at the outset we postulate that every one of the symbols used, does definitely represent some deity or other personification, who was believed by the possessor of the amulet to be a protector against maleficent influence. The combination
of symbols we find to be as various both in number and description, whether we take ancient or modern dates, as is now the cult of the various saints in the calendar; so that when we find an amulet of unusually complex character, bearing a great number of symbolic figures, we may take it to be the prototype and the equivalent of the latter-day summing up of "All Saints" or "all the company of heaven." A singular comment upon this accumulation of protectors is seen' in an inscription of the first year of our Christian era, A.U.C. 754, found quite recently in the Tiber near the Church of Sta. Lucia della Tinta.
Under the consulship of Caius Caesar and Lucius Paulus, a freedman named Lucius Lucretius Zethus was warned in a vision by Jupiter, to raise an altar in honour of Augustus, under the invocation of "Mercurius Deus Æternus." Following these directions, Lucretius Zethus had the altar made, and unwilling apparently to hurt the feelings of the gods in general, dedicated it not only to Mercury Augustus, but at the same time to Jupiter, Juno, Minerva, the sun, the moon, Apollo, Diana, Fortune, Ops, Isis, Piety and the Fates. From an epigraphic point of view, this monument ranks among the very best discovered in the works of the Tiber. 210
A great number of ancient compound amulets in the shape of marble reliefs, medals and engraved gems, have been found, in which an eye is the central object, while grouped around it are various animals or other emblems of protecting divinities.
Jahn in his well-known paper gives no less than six different medals and gems, which have for each the eye as a centre, surrounded by a greater or less numerous grouping of symbolic figures, and all are undoubted amulets of ancient date against the evil eye.
No. 2 in Jahn is taken from Caylus rec. vi, 38,
[paragraph continues] 3 (Fig. 14), and is a struck medal having in the centre the eye, surrounded by a crocodile, swan, serpent, cock, dog, lion, winged phallus, scorpion, and thunderbolt.
No. 3 (Fig. 15) is from Arneth, Gold- und Silbermon, S. iv. 96 G.--a medal with eyelet for

Click to enlarge
FIG. 14, 15, 16.
suspension. It has the eye in centre, with crocodile or lizard, thunderbolt, elephant, scorpion, phallus (as seen at Pompeii), lion, dog, swan, around it.
No. 4 is from Caylus rec. v. 57, 1, 2 (Fig. 16), also a medal with eye in centre, surrounded by thunderbolt, lizard, phallus, scorpion, star, elephant,
 Click to enlarge FIG 17. |
No. 5 (Fig. 17) is an engraved gem, from the Florence Museum. It has the central eye, with lizard, scorpion, frog, bee, serpent, crab, bee again, and tortoise, surrounding.
No. 6 (Fig. 17) also a gem from Antike Paste in Berlin, described by Winkelmann, p. 554. It has the eye in the centre with tortoise, lizard, scorpion, frog, bee, serpent, crab, and another bee, surrounding. 211
No. 7 (Fig. 18 is an engraved onyx 212 from Gerhard's collection, with central eye, but with Jupiter's or Serapis's head, eagle,
 Click to enlarge FIG. 18. |
Still more remarkable than any of the foregoing amulets given by Jahn is that of an engraved sard from the Praun gems, of which an illustration is given by King, Gnostics, p. 115, and also Handbook

Click to enlarge
FIG. 19.--From King's Gnostics.
of Engraved Gems, p. 81, where the central eye is surrounded by an owl, serpent, stag, scorpion, dog, lion and thunderbolt (Fig. 19).
On this blood-red gem King remarks (Gnostics, p. 238) that it shows "the evil eye surrounded by antidotes against its influence for every day in the week, in the attribute of the deity presiding over each, namely, the lion for dies Solis, the stag for dies Lunæ (Diana venatrix), the scorpion for dies Martis, the dog for dies Mercurii, etc." To these we must add the thunderbolt for dies Jovis. The owl, however, was sacred to Athene or Minerva, and must have been substituted as the symbol of dies Veneris, for Venus does not seem to have been regarded as a protectress against fascination, unless we look upon her as identical with Isis, Ishtar, and Diana; whereas Minerva, the bearer of the Gorgon's head, was always one of the most potent protecting deities. The serpent, too, was the symbol of Hecate, 214 one of the attributes, as we shall see later, of Diana Triformis, and was considered one of the most powerful of all the antidotes. Scarcely any compound amulet occurs without the serpent, and hence we must suppose in the case we are considering that it was adopted as the symbol applicable to dies Saturni. 214a
In considering this gem, we must not forget its Gnostic character, and that its origin was Græco-Egyptian, though the work of a European hand.
[paragraph continues] Hence every symbol must be interpreted as Egyptian from a Greek point of view. Now as we know, and as Pliny 215 long ago related that there are no stags in Africa, it is clear that the designer of this amulet must have denoted by the stag a deity of the Græco-Roman mythology; and we must therefore look for one whose prototype is to be found in Egypt, and whose attributes were the same as the Ephesian Diana whom undoubtedly the stag represented in his idea. This could be no other than Hathor, whom we must look upon like Diana, as distinctly a moon goddess. 216 So the thunderbolt, in like manner, would represent Serapis, the great Sun-god.
Thus considered, every one of the symbols on this week-day amulet ultimately resolves itself into one or other of the great Gnostic gods, the Sun and Moon.
The use of the eye as the central object in amulets involving sympathetic magic, may be taken to be universal. "Arab amulets at the present day bear the figure of the thing against which they exert their virtue, and all oriental practices in this line come down from immemorial antiquity." 217
The Maltese, partly Arab and partly Italian, holding the beliefs and customs of both parent stocks,
are specially in dread of the evil eye, and being a maritime people too, we should look for marks of this in connection with their principal calling, for perils by the sea are everywhere believed to be constant sources of danger subject to maleficent influence. Consequently we find the native boats, as a regular part of their decoration, have a large eye painted on each side of the bows, giving them a very weird and uncanny appearance, much enhanced by the high prolongation of the stem. The same kind of stem is seen in the Neapolitan boats, though without the eyes.
The writer has seen boats having eyes on either side of the prow in some other places, at Smyrna, or one of the Greek ports, but having missed his note cannot recall at which port it was. This custom is evidently of great antiquity. The eye was placed on boats by the ancient Egyptians, 218 and also by the Etruscans. 219 Dennis remarks: 220 "The presence of eyes on the bows of ancient vessels, perhaps originating in the fancied analogy with fish, or to intimate the vigilance necessary to the pilot, is well known--'they were charms against the evil eye.'" 221
Besides the conventional ouza or œil mystique already referred to, the Egyptians wore eyes as amulets of a more realistic character. They were in pairs, looking fully to the front, and were pierced

Click to enlarge
FIG. 21
with the usual hole for the string. A number of examples of this kind may be seen in the Ashmolean Museum at Oxford.
In the remarkable necklace or string of amulets found in a tomb at Kertch, taken by Jahn from the Russian work of Achik, 222 a great many of the separate objects have markings on them which can only be intended for eyes (Fig. 21).
Jahn, page 41, says that necklaces with separate pendants as amulets are extremely common in Etruscan art-work. Among other people, girdles of various kinds, arm-bands with amulets thereon, are common, and specially in Italian art-work.
 Click to enlarge FIG. 22 |

Click to enlarge
FIG. 23.
Maltese boats. It was in itself a powerful amulet,
and was therefore used as a conspicuous object of decoration.

Click to enlarge
FIG. 24--From Woburn Marbles.
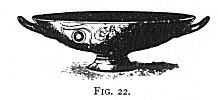
Fig. 22 is from Vulci. 223 Fig. 23 is an Etruscan winged deity. 224
Perhaps the most noteworthy of all the amulets in which the eye forms the central object in combination with several other emblems, is the very remarkable relief illustrated in Millingen's paper in vol. xix. of Archæologia, p. 74, and referred to by Jahn. 225 It is one of the Woburn marbles (Fig. 24) in the collection of the Duke of Bedford, and measures 1'6" x 1'5", but this last dimension is not perfect, being broken on the left side. There was a framing, and it is usually thought to have been built into a wall, as a house-decoration, but still more as a protection. The centre is a large human eye, and, as Jahn says, "the left, which may be considered a special feature of its sinister intention, and moreover the pupil is strongly marked." 226 Over it is a very prominent eyelid and an arched brow. Above this is seated a beardless man in a Phrygian cap, with his back towards the spectator, and his head turned backwards. He is squatted down with both hands on his knees, has his shirt pulled up, and strikingly exemplifies the description of Pomponius:--
"Hoc sciunt omnes quantum est qui cossim cacant." 227
[paragraph continues] Moreover it is evident that he is in that position which even now conveys in its full reality (in England no less than in Germany) the common
typical expression of the utmost contempt. 228 In fact, the figure is sitting on the eye in a most indecorous position, and as we explain later, any object or gesture which gave rise to an indecent or obscene idea was looked upon as specially effective in the way of a protection against fascination. One cannot help once more remarking here, how strikingly this mockery of the evil eye, this challenging of its malignity in the old Roman days of Septimius Severus, to which period this marble is ascribed, are reproduced in this enlightened nineteenth century by the heroic performances of the "Thirteen Club." Surely the dinner with its brave defiance of the Fates is a very eloquent and convincing piece of evidence that so-called civilisation, enlightenment, culture and all the rest of it, have not even yet eradicated the feeling, which has existed in man's breast from the remotest antiquity-that there is a power, an influence, a something passing from certain persons to others, which though unseen, unfelt, unmeasured and incapable of explanation, at least is dreaded by many, and perhaps most by some of those who scoff loudest, and outwardly defy it most ostentatiously.
It is well known that at the present day Neapolitan and other Italian sailors use this same identical attitude, turning themselves thus towards a contrary wind, in the belief that by such contemptuous defiance of the adverse spirit of the wind, its direction may be changed. 229
On the right of the spectator in our illustration is another figure with his face turned towards the Phrygian, the former appears to be a gladiator wearing the distinctive girdle called the subligaculum. In his right hand is the trident, with which he seems to stab the eye, and in his left a short sword 230 (fuscina). The yoke-like object on his left shoulder, and the armlet he wears, recognised as the galerus, 231 prove that he was a Retiarius, one of those who fought with a net, which he tried to throw over his opponent the Mirmillo, so as to entangle him and his shield; and then he attacked him with the trident. The Retiarius, moreover, used to fight bare-headed like the figure here. There was most likely (Jahn says, ohne Zweifel) a figure on the opposite side of the bas-relief, which is now broken off, and it is here suggested that the latter may have represented the opposing Mirmillo, though Jahn says nothing upon that subject.
On the lower part of the marble are five animals seemingly attacking the eye with great fury. These are a lion, a serpent, a scorpion, a crane, and a raven or crow--each one a distinct amulet in itself.
Millingen remarks that no doubt can be entertained but that the evil eye or fascinum is here represented, and in this opinion he is fully supported
by Jahn; while to any candid observer the relief itself is by far the best evidence. 232
It was usual to ornament the coffins or mummy cases of the ancient Egyptians with two large open eyes, with two monumental doors on the left, while on the right they placed three doors. These eyes could only have been intended to answer the same purpose on the outside as the œil mystique within.
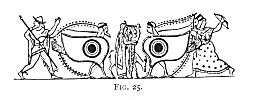
The remarkable scene here given (Fig. 25) from an amphora found at Vulci, now in the British
Click to enlarge
FIG. 25.
[paragraph continues] Museum, is but a sample of the eyes found on painted vases like this, not only of Etruscan, but also of undoubted Greek origin, which are fully recognised, says Dennis, as charms against the evil eye. 233
The curious representation of the great eyes (evidently the feature of the whole) upon the conventionalised wings of two Sirens, and upon those of a Fury in the collection of Sig. Bargagli at Sarleano, described by Dennis, 234 forms another connecting link in the chain which we hope to forge, by which we shall connect the sirens of modern Naples with
the ancient mythology of Egypt, Greece, and Rome. The Etruscans ornamented their vases and furniture with eyes very conspicuously depicted, as may be seen in the Museo Gregoriano in Rome and elsewhere. On these Dennis 235 remarks, that they "have evidently an analogy to those so often painted on the Hellenic vases, and have probably the same symbolic meaning."
The ancient Egyptians, too, were accustomed to
 Click to enlarge FIG. 26. |
Except upon Maltese and some other boats, or in masonic symbolism, the eye seems to have passed out of modern use, and as an amulet almost exclusively to be a thing of the past; even among the ancients it was by no means the commonest emblem used against its own influence. Eyes, however, made of wax or silver are extremely common to-day as ex votos--hung up in churches, before Notre Dame de bon secours, and some other favourite saints, such as SS. Cosmo e Damiano. We must ever bear in mind that it was, and continues to be, believed that the first glance of the evil eye was the
most fatal, and therefore it was of the utmost importance that any object intended to protect against its influence should be such as should attract the first or fatal stroke; for it was just as firmly held, that whatever diverted it for the moment from the person or animal liable to injury, absorbed and so destroyed its effect. Anything, therefore, calculated to excite the curiosity, the mirth, or in any way to attract the attention of the beholder was considered to be the most effectual. There were three methods generally accepted for averting fascination, whether it were of look, voice, touch, or bodily presence of the fascinator. 237 These were, by exciting laughter or curiosity; by demonstration of good fortune so as to excite envy in the beholder and so to draw his evil glance upon the object displayed; and by doing something painfully disagreeable to cause him an unpleasant feeling of dread lest he, the fascinator, should be compelled to do likewise. 238
Plutarch in a remarkable passage 239 declares that the objects that are fixed up to ward off witchcraft or fascination, derive their efficacy from the fact that they act through the strangeness and ridiculousness of their forms, which fix the mischief-working eye upon themselves. 240
It was this firm belief which led to the design of those extremely grotesque figures amongst the Romans of which they were so fond, and of
which we have such numberless examples in every museum of ancient gems. These amulets, all intended for the same purpose, are now called
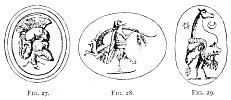
Click to enlarge
FIG. 27., 28., 29.
[paragraph continues] Grylli, from modern Italian grillo, signifying both a cricket or grasshopper, and also a caprice or fancy. 241
 Click to enlarge FIG. 30 |
These grotesques formed of the creatures, sometimes called Chimeræ, have been by some considered as Gnostic remains; but it is urged on the other side, 242 that besides never exhibiting the symbols which are characteristic of Gnosticism, the style of work proclaims them to the least experienced eye to belong to a much earlier date--that of the best period of
Roman art. 243 In any case the strange combination of various animal forms in one is certainly a practice handed down from ages long antecedent to either
Click to enlarge
FIG. 31., 32., 33.
Gnosticism or Roman history. Early Etruscan bronze amulets were very commonly formed by
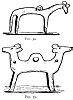 Click to enlarge FIG. 34., 35. |
in Christian art been separated and become the symbols of the four Evangelists.
In treating of amulets it behoves us to give an early place in our consideration to that which of all others may be taken as the first, the original germ,
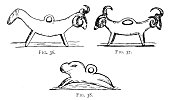
Click to enlarge
FIG. 36., 37., 38.
at least so far as noticeable in Greek art--the head of the Medusa, or as it is commonly called, the Gorgoneion.
The story of Perseus and of his killing the Medusa, whom he only ventured to look at in a mirror, need not here be detailed, but in it we have at least a very early incident in the primæval belief in the evil eye. So far as Greek art goes, we have in the hideous representation of her dog-toothed, split-tongued visage, the earliest example which we can positively assert to be a prophylactic charm against the fatal glance which she was believed to have possessed; for though there are plenty of Egyptian
amulets of earlier date, it cannot be certainly declared what was their precise intention. This very remarkable object is of so much importance that we must make it a subject to be treated apart; 244 suffice it here to say that from being the earliest of amulets known to European art, so the illustration on p. 160, Fig. 49, shows it to be one of the latest, if not the latest, used in Christian times to baffle the evil eye. We also see by the same illustration that it is one of the most debased among the many examples of declining art. It is of course out of our province, and beyond our ability, to decide whence the Greeks obtained the story, and we must leave that question to experts who are content to contract more narrowly their investigations. The obvious development of the early idea of the Gorgon's head, from its first conception of the intensest ugly frightfulness, until it became at last by the gradual refinement of taste, as shown in classic art, the ideal of female beauty, culminating in the well-known Strozzi Medusa, 245 demands careful attention.
The step from the famous death-dealing visage, as a protection against the very evil it was believed to produce, is but short to that of hideous faces in general; and hence we find that strange and contorted faces or masks were certainly used as objects to attract the evil eye, and so to absorb its influence, and to protect the person wearing or displaying the mask. The very origin of the name mask is said to be but
a corruption of the older Greek βασκα, whence βασκανία, fascina or amulets. "From this custom of regarding hideous masks as amulets can be explained a circumstance otherwise a problem to every archaeologist--the vast number of such subjects we meet with in antique gems." 246 Not only so, but their importance is still more impressed upon us by the fact that the highest skill known to Roman art was lavished upon the engraving of masks.
Nothing, as is well known of all ages, so much attracts or excites curiosity as obscenity and indecency; 247

Click to enlarge
FIG. 39., 40.
and hence of all amulets, those partaking of this character were the most potent, and therefore the most used. Anything strange, odd, or uncommon, as likely to attract the eye, was considered most effectual, and consequently the objects viewed as protective against it were almost infinite in number. For the reasons given we find in compounded amulets that the commonest of all objects was the phallus, or some other, suggesting the ideas conveyed by it.
Amulets then which protect against the power of fascination would naturally be of three classes. First, those whose intention was to attract upon themselves the malignant glance. These were necessarily either worn on the outside of the dress, or openly exposed to view like the grillo of Pisistratus at Athens, the brazen serpent set up by Moses, or the various household objects displayed for the same purpose. Secondly, there were all those charms, worn or carried secretly, or hidden beneath the dress; and thirdly, the written words of Scripture, Koran, and other sacred writings, or the cabalistic figures and formulæ considered so powerful.
The former class were the most numerous, and of them we have the greatest number of examples, both ancient and modern. For the reason above stated, amulets consisting alone of das männliche Glied, or compounded with it as the attractive feature, were so common that they obtained a technical name from the purpose they were intended to serve. The usual term among old writers was fascinum. 248
Other writers, especially Varro, call one particular form which was commonly suspended from the necks
of children turpicula res, scæva or scævola, and he discusses at some length the development of the word. 249
Dodwell (vol. ii. p. 34) says: "They are frequently found in Italy of bronze, and the other extremity of the symbol is terminated by a hand which is closed; the thumb protruding between the fore and middle fingers. 250
This is but a very partial description of a most remarkable object much easier portrayed than described. It is of so obscene a character that it cannot here be reproduced.
A full-sized illustration of one in bronze from the Dresden collection is given (p. 81) in Jahn's Ueber den Aberglauben, etc. It is evidently a pendant-amulet, having three extra eyelets, from which probably little bells were hung, such as will be seen later on in our illustrations of the Sirens and Sea-horses. One branch of the pendant consists of a phallus such as Frommannd describes (p. 5), tam rigidum reddere quam cornu; while to balance it, is an arm ending in a fist with the thumb protruding as stated by Dodwell. The central part or body is composed of another membrum, of the kind constantly found as a separate amulet. Any number of these may be seen both as amulets and as ex votos in the private Museum at Naples, and also in the Museum of the Collegio
[paragraph continues] Romano. A very beautiful specimen of a turpicula res is in one of the cases of antique jewellery in the Louvre Museum. It is of gold, and measures about an inch and a half wide, and itself forms the pendant to a complete necklace, having above it as part of the pendant a fine amethyst cut as a scarab. There may be others in other museums, but the above is by far the most elaborate known to me, and is a most interesting study. In the same case are several other amulets against the evil eye, among which is the medal (Fig. 12).
In the Naples Museum are many bronze examples of various sizes, but all similar in pattern; in all cases the thumb is between the first and second fingers. There are also many phalli with eyelet holes to enable them to be worn as charms.
The vast antiquity of the phallic necklace can be easily demonstrated: it was very ancient even in the days of Horace and Varro; and it may be that the Romans got their fascinum from Egypt. In a recently discovered tomb at Thebes, near that of Rekhamara, the account of which has not yet found its way into the guide-books, the writer was struck by a singularly fresh and distinct painting of a necklace--the colour as bright as the day it was painted, more than three thousand years ago. It is formed of a chain fastened by a serpent's head, such as may be seen in our own shops to-day. The ornaments are three pendants--the phallus, 251 the most conspicuous, in the centre, the symbol of stability, and the ankh, or symbol of life, on either side.
[paragraph continues] The necklace so carefully painted is being presented by one female figure to another, but there are no special attributes by which to decide whom they are meant to represent. The attitude of the figures, and the prominence given to the three pendants of the offering, show that it was intended to be received and worn as a protective amulet.
Although of course the turpicula res is no longer to be found in actual use, yet the fist with protruding thumb is to-day one of the commonest of objects
 Click to enlarge FIG. 41 |
very different is worn by the babies in Naples and Southern Italy.
In making purchases of this and of the many other charms in the writer's possession, it has always been his practice to inquire of the seller what was the object of the article. In every case the answer has been the same--"Contra malocchia" in Rome; "Contra la jettatura" in Naples.
The antiquity of the phallus as an amulet is shown by the number found among Egyptian sculptures. No visitor to Egyptian antiquities needs to be told this. Indeed, it was held to have been consecrated by Isis herself. 252 The phallus was the most sacred amulet worn by the vestal virgins of ancient Rome. 253 Moreover, we find that Sesostris of the early twelfth dynasty, who conquered Asia, set up memorials of a phallic nature among the people who had acted bravely, but among the degenerate, female emblems engraved on stelæ were set up. 254 Who shall say these objects may not have been the origin of those still to be found so universally throughout India? In the ruins of Zimbabwe, in Central Africa, are to be seen phalli carved upon stone, similar to those found in Sardinia, which are said to be Phœnician. 255 The like have been seen by the writer on the so-called Phœnician ruins of Hajar Khem in Malta. Again, numbers of phallic amulets in bronze are found in the earliest Etruscan tombs as well as in the museums of the Collegio Romano, of Cortona and of Bologna, marked
as belonging to the prima età di ferro--a time which, like Egyptian monuments, makes the objects of Classic Rome things of yesterday. The objects on Fig. 42 are in the Museum at Bologna. In the Naples Museum are a number of vases of different shapes, ornamented with vine leaves and tendrils
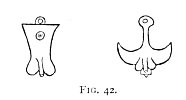
Click to enlarge
FIG. 42.
alternating with a phallus, forming a belt of decoration round the belly of the vase.
The object described as satirica signa by Pliny, and so constantly referred to, appears not only upon the amulets of which the eye is the centre, but is that to be seen over so many of the doorways in Pompeii. It by no means signified that which the ciceroni now tell the tourist; 255a but was placed there as a protective amulet against fascination. We read 256 that it was the common sign over a blacksmith's forge, and no doubt inasmuch as the horses who came to him to be shod were specially liable to the malign influence, so the smith would naturally provide the best possible protector for the animals by whom he got his living.
"That such representations were placed by the ancients on the walls of their cities, there is no lack of proof. 257They are found on several of the early
cities of Italy and Greece, on masonry polygonal as well as regular." At Alatri it is tripled, sculptured in relief on the lintel of a postern or passage in the polygonal walls of the citadel. It is also tripled on the Pelasgic walls at Grottatore. Another is found on the ancient wall of Terra di Cesi, near Terni, and again on the ancient fortifications of Todi on the upper waters of the Tiber, where it is in high relief, and is well known as il pezzo di marmo. There is one on a block in the wall of Oea, in the island of Thera in the Ægean Sea, with an inscription accompanying it, which distinctly proves it to have been intended to avert the evil eye. The same thing has been found on the doors of ancient tombs at Palazzuolo in Sicily, at Castel d'Asso in Etruria, and in the Catacombs of Naples. Of all places, however, the greatest number now to be seen are amongst the tombs and temples of Egypt.
Jahn gives plates of a very remarkable kind, of objects sculptured on the amphitheatre at Nismes, to be seen at the Dresden and other museums; he pursues this subject at greater length than can be here followed. To have omitted all notice of it would have been to leave out really the part on which ancient and mediæval writers have dwelt longest; still it is unsavoury, and we are glad to have done with it, the more so as we have so many facts and objects to be found in the life of to-day which seem to have been singularly overlooked by those who have written on the evil eye.
Repeated mention is made in these pages of the many amulets to be found in the Etruscan Museum at Bologna. Of the accompanying illustrations, Fig. 43 is taken from Burton's Etruscan Bologna,
p. 68, who gives it as a pelekys or axe, which he says is an amulet against fascination. Fig. 44 is from a sketch by the writer from the same museum.

Click to enlarge
FIG. 43., 44.
[paragraph continues] It also suggests an axe in shape, about one and a half times the size of illustration, and from its being evidently for suspension, it is here suggested that it may be an amulet. Being of bronze, and very thin, it is possible that its use may be the same as the
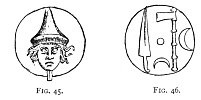
Click to enlarge
FIG. 45., 46.
very numerous handled half-moons of about the same size, found there and in other museums, which are well known to be ancient razors. In the object here shown, there is but one possible cutting edge, that at the bottom. Figs. 45, 46 represent an Etruscan coin 258 of the town of Luna. The devices engraved upon it almost certainly prove that they
were intended as amulets. The axe and sword were each considered to be such, while as to the two crescents, we may accept one as being a rebus of Luna, and the other to be the consort of the central solar disc. The head on the reverse may be the personification of the city or of Diana.
116:182 La Migration des Symboles, Comte Goblet d'Alviella, Hibbert Lectures, 1890-91: Husenbeth, "Emblems of the Saints in Art," Spectator, June 29, 1889.
116:183 Chapman, Sermons on Symbols, 1888.
118:184 "Emblema licet cum isto ænigmatum genere in ratione symboli conveniat, differt tamen, quod rem sublatis ænigmatum velis purius liquidiusque proponat. Est enim proprie symbolum aliquod ingeniosum, suave, et moratum, ex pictura et lemmate constans, quo aliqua gravior sententia indicari solet."--De symbolica Ægyptorum sapientia. Nicolaus Caussinus. Coloniæ, 1623, p. 17.
119:185 "On the main gateway of the Old City (Citta Vecchia) at Malta is a statue of Juno, ancient protectress of Malta, bearing her cognisance of a peacock."--Col. R. L. Playfair, Murray's Handbook to the Mediterranean, 1882, p. 199.
119:186 Notes and Queries, 8th ser. iv. p. 531 (December 30, 1893).
120:187 Mrs. Gaskell in Nineteenth Century, February 1894, p. 264.
120:188 See Notes and Queries, November 25, 1891 p. 426.
120:189 New English Dictionary, s.v. "Amulet."
121:190 See The Gnostics, by C. W. King, 1874, p. 115. Also Frommannd, Tract. de Fasc. p. 278, who makes a long disquisition on this subject, giving the etymology and origin of talisman as Arabic.
121:190a King, op. cit. p. 115. According to N. E. Dictionary, "a word of unknown origin."
121:191 Natural History, xxv. 67 (Bohn, v. p. 125).
121:192 Notes and Queries, 1st ser. vii. p. 496.
121:193 On this see Lobeck, Aglaophamus, p. 973.. He quotes Pliny, xxix. (6) 39, but I cannot find this in Pliny. Lobeck says Hesychius calls this amulet κερομία προσβασκάνια.
122:194 King, Gnostics, p. 116.
122:195 Ibid. p. 2 12.
122:196 Genesis xxxi. 19. See Frommannd, Tract. de Fasc. p. 715, who says Luther called these Silberne Götzen. These are called teraphim in the R.V.
122:197 Professor Huxley says (Science and Hebrew Tradition, 1893, p. 309): "The teraphim were certainly images of family gods, and as such in all probability represented deceased ancestors," and further that Jacob was not "scandalised by the idolatrous practices of his favourite wife . . . for the teraphim seem to have remained in his camp." Other authorities say (Reginald Stuart Poole in Smith's Dict. s.v. "Teraphim, Magic." Also W. Aldis p. 123 Wright, s.v. "Nehushtan ") "there is no evidence that they were ever worshipped. "There seems to be a consensus of opinion that the teraphim, whatever they were, had much to do with magic. It is here suggested that many of the numberless little bronze statuettes, to be seen in various museums, probably represent the Teraphim of the Hebrews and the Lares of Rome, and are not mere ornaments. Fig. 105 is surely one of these, and its original cannot be later than the time of Jacob. The terra-cotta figures too, beginning with the crude forms found at Mycenæ, and developing into the beautiful artistic statuettes of later Greece, must have been of the same character; for we cannot suppose that as mere ornaments they would have been so carefully deposited along with the dead. Nor does there appear to be any evidence that the Greeks or Romans ever imbibed the Egyptian notion of placing figures of this kind with the dead, as ushebtiu, to attend on the departed in the next world.
It seems rather an assumption than a certainty that teraphim were images only of persons. It is suggested that among such may be included several other objects, looked upon as prophylactic, or otherwise sacred. The bronze bands, dealt with in the chapter on the Mano Pantea, would distinctly come into this category. Further we find proof of this in the point noticed by Huxley (p. 310), that it was not until the time of Hezekiah that the brazen serpent of Moses was destroyed. During the thousand years of its existence it had been preserved, and at length from a protective teraphim had become Nehushtan. All this seems to show that the brazen serpent, and all such objects as we now call amulets, like the grillo of Athens, the crocodiles of Seville and Venice, were not originally worshipped idolatrously, but were looked upon as magically endowed with the power of countervailing the effect of the malignant eye--the fertile source, as it was thought, of every evil to mankind.
It has been well suggested (Farrar in Kitto's Cyclopædia of Biblical Literature, s.v. "Teraphim") that the teraphim, and to them we would add protective symbols in general, were looked upon much in the same way that pictures and images are now looked upon by Roman Catholics, who indignantly repudiate the notion of idolatry. No doubt the denunciations of the prophets point to the same line of teaching as that of modern Protestants, who can perceive no difference between the reverence paid to the image itself, and that which all would admit to be due to the person depicted.
123:198 Smith's Dictionary of the Bible, s. v. "Amulets."
124:199 Upon this, see Farrar in Smith's Bib. Dict. s. v. "Frontlets."
124:200 See the remarkable Ethiopic charm in Chap. XI.
125:201 Wilkinson, Ancient Egyptians, iii. 130.
125:201a Ib. iii. 80.
125:202 Plutarch, De Iside, s. 32; Wilkinson, iii. 74.
125:203 Archéologie Egyptienne, p. 236. See also Wilkinson, vol. iii. p. 486.
126:204 Brugsch, Egypt under the Pharaohs, vol. i. p. 468. Wilkinson, vol. ii, p. 334, gives a number of necklaces, in nearly all of which the mystic eye appears, while in some it is the only element, and in others is alternated with other charms.
126:205 The Nile, E. Wallis Budge, p. 61.
126:206 One of these processions showing the eye is given as Plate lxvi. in Wilkinson, vol. iii. p. 444.
126:207 In the British Museum is a case full of these mystic eyes of all sizes. There are also necklaces composed entirely of them. Three of these in blue enamel are shown on Fig. 81.
127:208 See Dennis, Cities of Etruria, vol. i. p. 471.
128:209 It is suggested that the head here produced may be that of the Gnostic god Abraxas, who is very frequently represented with the head of a cock. See the many engraved gems showing this in Abraxas seu Apistopistus Johannis Macarii. Antwerpiæ, 1657. Also in King's Gnostics.
129:210 Rodolfo Lanciani, Athenæum, No. 3313, April 25, 1891, p. 543.
130:211 Nos. 5 and 6 have precisely the same objects upon them, though differing in size. Therefore one illustration here applies to both.
131:212 This gem is a cameo, upon which it may be remarked, that this word is said to be Persian. "Camahem is a loadstone or fibrous hæmatite, the usual material for Babylonish cylinders, and in use there down to the time of the Cufic signets. The Arabs knowing no other motive for engraving of stones than their conversion into talismans (amulets), gave the name of the one most frequently used to the whole class; and the Crusaders introduced it into all European languages in this sense. Matthew Paris has lapides quos cameos vulgariter apellamus, which marks its foreign origin" (King, Gnostics, p. 112). Mr. King does not give his authority. Dr. Murray (N.E.D.) says, "Of the derivation nothing is yet known." I do not find the above among the "guesses" alluded to by Dr. Murray.
131:213 The value of medals whether to be worn as amulets, or used as talismans to procure objects desired, or to cure diseases, is by no means a notion confined p. 132 to the ancients. In Ireland "some five-and-forty years ago a temperance medal was found to be a specific for every ailment; not all medals, however, but only those which had been blessed and given by Father Mathew. Rubbing with one of these at once relieved rheumatic pains. I have seen ophthalmia treated by hanging two of these medals over a girl's eyes" (Le Fanu, Seventy Years of Irish Life, 1894, p. 114).
132:214 Jahn, Aberglauben, etc., p. 98, says that "the dog as the beast of Hecate has to do with all magic" (Zauberwesen). In later times it was thought that by dogs' blood all evil witchery could be kept off.
132:214a Since this was written the Python at the Zoo has (Oct. 1894) swallowed his mate (or his child?), thus proving the serpent to be a singularly practical symbol of Saturn.
133:215 Pliny, Nat. Hist. viii. 51 (vol. ii. p. 302, Bohn). Diana is often represented as accompanied by a dog, the most sagacious and watchful of animals. The dog was a symbol of Diana, Thoth, Hermes, Mercury, Anubis (Payne Knight, Symb. Lang. p. 113). "The dog as a symbol of destruction was sacred to Mars as well as to Mercury" (Phurnutus, Nature of the Gods, xxi); hence "the dogs of war."
133:216 See the story of Osiris and Isis-Athor in Wilkinson, iii. 75 et seq.; also of Isis and her connection with the Dog-star, Ib. p. 106.
133:217 Cesnola, Cyprus, 1877.
 Click to enlarge FIG 20. |
134:218 Wilkinson, vol. iii. p. 353.
134:219 In the Grotta de Cacciatore, near Corneto, "is depicted a boat with a high, sharp stern and a low bow, on which is painted an enormous eye--a fashion that has descended from Etruscan times to the fishermen of modern Italy" (Dennis, Cities of Etruria, vol. i. p. 312).
134:220 Ibid. vol. i. p. 471.
134:221 On a vase in the British Museum representing Ulysses (tied to the mast) and the Sirens, the vessel has a large eye upon the prow--suggesting that another was upon the other side not seen. A plate of this is given in Smith's Classical Dict. p. 784, ed. 1877
136:222 Achik, Antiq. du Bosphore Cimmérien, vol. iii. p. 210. See also Daremberg et Saglio, p. 257.
137:223 Dennis, Etruria, vol. i. p. cxxi and p. 462.
137:224 Ib. vol. ii. p. 160. All the illustrations from Dennis are reproduced by the kind permission of Mr. John Murray.
138:225 The illustration here given is from Millingen's original plate, and differs in many respects from the copy of it attached to Jahn's article.
138:226 In consequence of the stress laid by Jahn upon the eye represented being the left, I have carefully examined all the eyes upon amulets which have come under my notice, and among a great number of examples I have found no marked preponderance either way, but on the whole should say there are more right eyes than left. The very common phrase "sinister expression," come to us from classic days, may have suggested to Jahn the idea that the left eye is especially malignant, but I can see no evidence in support of it, and believe the phrase has no connection with the evil eye, but that it springs from another and quite different set of beliefs.
138:227 Nonius, see cossim, p. 40, verb incoxare, p. 39. Jahn, p. 30.
139:228 Striking examples of this act have not long since come under the notice of the writer, in one of which a man used this means of grossly insulting a woman--about his equal in refinement--with whom he had had a quarrel.
139:229 This gesture was evidently of widespread use in ancient times. We are told that in the ceremony of going down the Nile to the festive worship of Bast at Bubastis the crowded boats, as they passed near a town, came close to p. 140 the bank. "Some of the women continue to sing and strike cymbals; others cry out as long as they can, and utter reproaches against the people of the town, who begin to dance, while the former pull up their clothes before them in a scoffing manner" (Herodotus, ii. 60, quoted by Budge, Nile, p. 111).
The writer can testify to having witnessed a similar performance by a woman on London Bridge at ten o'clock in the morning!
140:230 The trident and sword are separate amulets, as shown later.
140:231 This is taken from Jahn, p. 30, but according to Smith, Dict. of Gr. and Rom. Antiq., the galerus was a helmet or head-dress.
141:232 On the other hand, in the same volume (xix. of Archæologia, at p. 99), the Rev. Stephen Weston contests this view, and tries to prove that the whole piece of sculpture is a representation of the sacred rites of Mythra; but his views in support of his Mythraic theory are speculative and fanciful in face of the materialistic story of the marble itself. Upon this point Jahn, p. 31, says: "Es kann kein Zweifel sein und ist von allen erkannt, dass es bestimmt war Schutz gegen den Zauber des bösen Blicks zu gewähren."
141:233 Dennis, Etruria, vol. i. p. 471.
141:234 Ib. ii. p. 364.
142:235 Dennis, Etruria, vol. ii. pp. 77, 331.
142:236 It is the rounded bottom of a blue bowl. The fish here compounded with l'œil mystique, and the no less mystical lotus, is undoubtedly the sacred Lepidotus, fully described by Wilkinson (vol. iii. pp. 340 et seq.). It surely is not unreasonable to consider that a form of decoration common to Egyptians, Etruscans, and Greeks was not a mere coincidence, but had a well-understood common significance. The original bowl is in the Berlin Museum. The same illustration is in Wilkinson, vol. ii. p. 42.
143:237 "Fascinatio est actio, qua corpori noxa visu, verbis, contactu aut effluviis malis occulto modo agentibus per vim seu naturalem seu supernaturalem inferri putatur."--Frommannd, p. 7.
143:238 These are thus summed up by Vincentius Alsarius ("De Invidia et Fascinatione," Thesaur. Antiq. Rom. vol. vii. p. 890): "Quodam ridiculo spectatoribus objecto: . . . fortunæ secundæ dissimulatione; . . . casu aliquo adversa sponte suscepto et contractu," quoted by Frommannd.
143:239 Symposia, v. 7.
143:240 See remarks on Gurgoyles, Appendix II.
144:241 The alternative meaning of grillo in modern Italian is said to be a classic survival: "Antiphilus jocosis nomine Gryllum deridiculi habitus pinxit, unde id genus picturæ grylli vocantur" (Pliny, Sympos. xxv. 3 7).
144:242 King, Handbook of Engraved Gems, p. 81. The four grylli here reproduced are from Mr. King's books. I am indebted to Mr. David Nutt and Messrs. George Bell and Sons for permission to copy them.
145:243 It is certain that as works of art a vast number of the objects used as amulets were of a very debased kind indeed; but it should always be remembered that the virtue of an amulet or talisman lay in the type it embodied, and in its own material substance--the manner of execution of the potent sigil was altogether unconsidered. This will become abundantly plain when we come p. 146 to consider the very rough and crude objects made in these latter days for constant use in Naples-where the thing represented is of the rudest, coarsest work, while all the time it is of the most imperative necessity that each article should be of sterling silver, which must be attested by the hall-mark.
147:244 Jorio, Mimica degli Antichi, p. 235, says: "The common people (of Naples) are absolutely ignorant of everything concerning the Medusa's head; but they are fully persuaded that the eyes of the Basilisk (of which also they know nothing) have the same power as that attributed to the fabulous head."
147:245 Another beautiful Medusa is that upon the Onyx cup in the Naples Museum, called the Tasse Farnese. A print of this is in Daremberg et Saglio, Dict. des Antiq. p. 103.
148:246 King, Handbook of Gems, p. 85. Figs. 39, 40, come from a number of these masks in Mr. King's books, namely, the above and The Gnostics.
148:247 "Everything that was ridiculous and indecent was also supposed to be inimical to the malignant influence of fascination by the oddness of the sight," Dodwell, Class. Tour through Greece, 1819, vol. ii. p. 34.
"Quid? quod libelli Stoici inter Sericos
Jacere pulvillos amant?
Illiterati num minus nervi rigent,
Minusve languet fascinum?
Quod ut superbo provoces ab inguine
Ore allaborandum est tibi."--Horace, Epodon viii. 15.
[paragraph continues] (This epode is omitted in the expurgated editions.) See also Frommannd, Tract. de Fasc. p. 5, who says: "Per fascinum virile membrum, quod fascia tegi solet sive campestribus, hic intelligi Commentator et Cruquius dicunt. Fascinum autem vocarunt partem illam, quoniam fascinandis rebus hæc membri deformitas apponi fuit solita."
He goes on to connect the reason of the name with the licentious cult of Liberus. He also writes much on the subject which is unfit to be reproduced here, referring frequently to the worship of Priapus, and to the sayings of Enothea, priest of Priapus.
150:249 "Potest vel ab eo quod pueris turpicula res in collo quædam suspenditur, ne quid obsit bonæ scævæ causa: unde scævola appellata. Ea dicta ab scæva, id est sinistra, quod quæ sinistra sunt bona auspicia existimantur: a quo dicitur comitia aliudve quid; sic dicta avis, sinistra quæ nunc est. Id a Græco est, quod hi sinistram vocant σκαίαν: quare quod dixit Obscœnum Omen, est omen turpe, quod unde (id) dicitur, Osmen ex quo S extritum."--Varro, De Lingua Latina, viii. 97. Ed. Sprengel, Berlin, 1885.
150:250 "Inserto pollice inter medium et indicem, ita ut pollex ipse insertus emineret, et apparet, reliquis digitis in pugnum contractis."--De Pollice, p. 42, Lipsiæ, 1677.
151:251 Upon the importance of the phallus, and its consecration to Osiris, with the reasons for the place it took in the Egyptian system, see Wilkinson, vol. iii. p. 77, and various notices in vols. i. ii. concerning the God Khem.
153:252 Wilkinson, iii. p. 77.
153:253 Smith's Dict. of the Bible, s.v. "Fascinum."
153:254 Wilkinson, op. cit. i. p. 20.
153:255 Bent, Ruined Cities of Mashonaland. Perrot and Chipiez, History of Art in Sardinia, p. 57. Spectator, November 26, 1892.
154:255a That houses so marked were Lupanari.
154:256 Dennis, Cities of Etruria, vol. ii. p. 119. It was of course not confined to this purpose at Pompeii.
154:257 Dennis, as above. He refers to Pliny, but cannot find the passage. Dennis believes in their being thus placed to defy the enemy. I recommend the student to read this chapter.
156:258 From Dennis's Etruria, vol. ii. p. 63.